Week 5: Programming Robot Sequences with Blinking LEDs...
Read MoreWeek 7: Programming a Line Following Robot with IR Sensor
In Week 7, students will program a line-following robot using a single IR sensor and the L298N motor driver. The robot will turn left when the sensor detects a black line and turn right when the line is not detected. This exercise focuses on using sensor input to control motor movement for autonomous navigation.
- Successfully program the robot to follow a line using a single IR sensor.
- Demonstrate understanding of integrating a sensor with motor control.
- Ensure accurate wiring and code to achieve desired robot behavior.
- Adhere to safety protocols and collaborate respectfully with peers.
- Review of Line Following Concepts
- Connecting Motors and IR Sensor
- Programming Line Following Behavior
- Testing and Debugging
- Practice Session
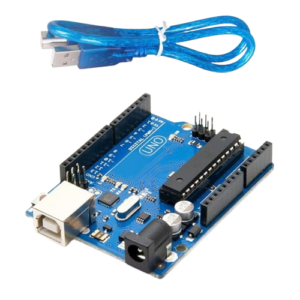
Arduino Board
- Function in Project: Acts as the main microcontroller to run the program and control the LED.
- Other Real-life Uses: Can be used in robotics, home automation, weather stations, and many other DIY electronic projects.
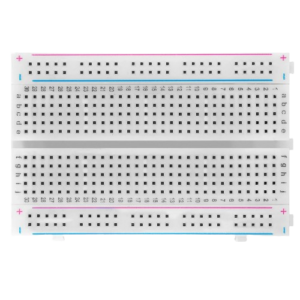
Breadboard
- Function in Project: Provides a platform to build and test circuits without soldering.
- Other Real-life Uses: Useful for prototyping circuits in electronics development and for educational purposes.

Jumper Wires
- Function in Project: Connect different components on the breadboard and to the Arduino.
- Other Real-life Uses: Used for making temporary connections in testing and prototyping electronic circuits.
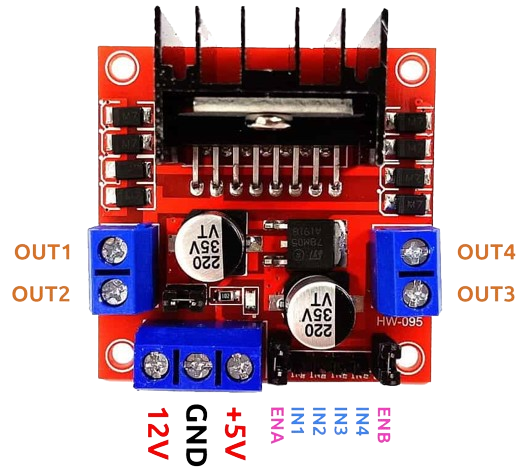
L298N Motor Driver
- Function in Project: Controls the speed and direction of the motor.
- Other Real-life Uses: Used in various robotics and motor control applications to drive DC and stepper motors.

Gear Motors
- Function in Project: Converts electrical energy into mechanical movement to drive the robot forward.
- Other Real-life Uses: Used in fans, toys, and various mechanical devices requiring rotary motion.
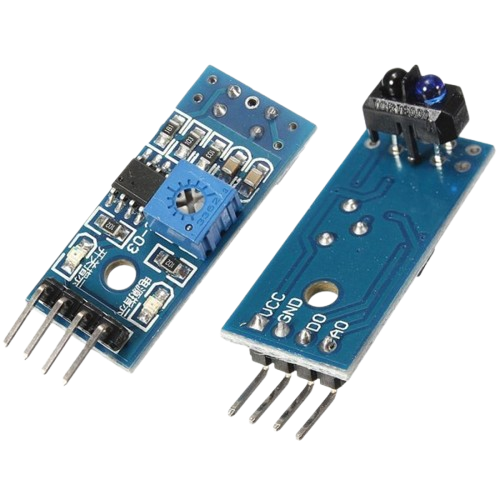
TCRT5000 IR Sensor
- Function in Project: Detects the presence or absence of an object and sends corresponding data to the Arduino.
- Other Real-life Uses: Used in line-following robots, object detection, and other sensor-based applications.
Review of Line Following Concepts
Understand the basic principles of line-following robots.
Line Following: The robot uses an IR sensor to detect a line and adjust motor speeds to stay on track. In this case, it will turn left when the line is detected and right when it is not.
Connecting Motors and IR Sensor
Wire the motors and IR sensor to the Arduino and L298N Motor Driver.
Steps:
- Motor Connections:
- For 2 motors: Connect each motor to OUT1/OUT2 and OUT3/OUT4 terminals on the L298N.
- For 4 motors: Connect two motors to OUT1/OUT2 and OUT3/OUT4 each.
- IR Sensor Connection:
- Connect the IR sensor output to a digital pin on the Arduino.
- Power the sensor using the 5V and GND pins on the Arduino.
- Motor Connections:
#include <RoboticCar.h>
int EnA = 3;
int In1 = 4;
int In2 = 5;
int EnB = 6;
int In3 = 7;
int In4 = 8;
RoboticCar myrobot(In1, In2, In3, In4, EnA, EnB);
int sensorPin = 2; // IR sensor connected to digital pin 2
void setup() {
pinMode(sensorPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = digitalRead(sensorPin);
if (sensorValue == HIGH) {
// Black line detected
myrobot.left(200); // Turn left
} else {
// No black line detected
myrobot.right(200); // Turn right
}
}
Objective:
- Test the robot’s line-following capabilities and make necessary adjustments.
- Refine the robot’s line-following performance through experimentation.
Activity:
- Place the robot on a track with a black line.
- Observe and adjust the robot’s behavior to ensure it turns left when the line is detected and right when not.
- Test the robot on different track layouts and make adjustments as needed.
- Experiment with different speeds and turning angles to optimize performance.
4WD robot 4
Week 4: Programming 4 Motors with L298N Motor...
Read More4WD robot 3
Week 3: Programming 1 Motor to Drive Forward...
Read More4WD robot 2
Week 2: LED Blink and Patterns Summary In...
Read More